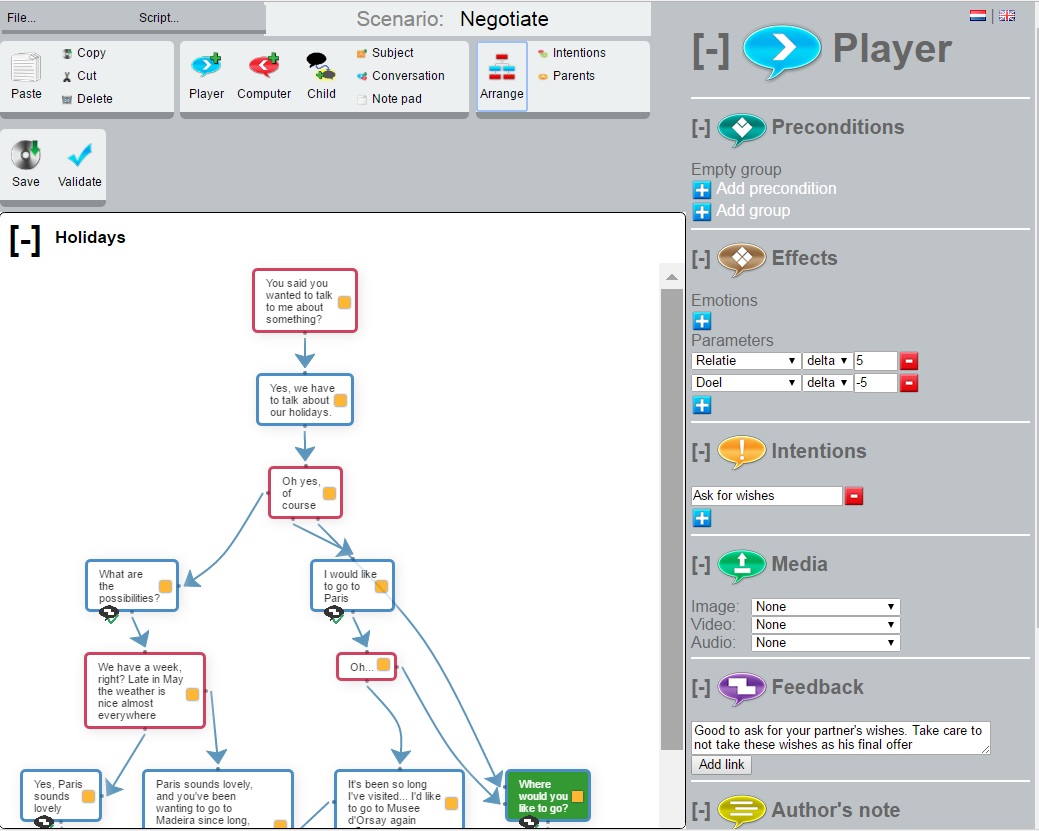
Dialogue Scenario Editor
- Creator: Utrecht University email
- Publisher: Rage project
- Owner: Johan Jeuring email
An author / communication expert can develop a dialogue between a virtual character and a player / user in this tool.
Short non-technical description: A dialogue consists of statements between a player and a virtual character, in which a player choose between various pre-specified statements. The editor balances usability for a non-programming (communications) expert and expressiveness of the constructs in which a scenario can be expressed.
Technical description:
A communication expert / author develops a communication scenario as a directed acyclic graph of steps. A scenario can be used for dialogue in a game /simulation.
The editor has the following basic features:
- Develop a conversation between a virtual character (computer node) and a player as a graph. The graph is from top to bottom in time.
- Choices for a player are as multiple player statements from a computer node.
- Each player statement choice leads to a score, and effects like emotions in the virtual character.
- A statement can have a condition.
A domain expert can then export valid scenarios in XML format. Scripts may be saved locally and imported to modify and continue development.
Detailed description:
Conversations can be structured at a higher level of abstractions in subjects. A subject on the horizontal level is interleaving with another subject(s) on the same level. During the simulation a player is presented with statement choices from within these interleaving subjects without a predetermined order. This is useful when a player should communicate with a virtual character on multiple subjects, but the order in which statements within these subjects are followed is not important. A subject may be marked as optional, which means that the subject may be skipped in simulation.
Subject variability is augmented with statement variability. In addition to conditionality in nodes, three features that a scenario author may specify on a computer statement are ‘Jump to another subject’, ‘Early end of scenario’ and ‘End of scenario’.
A ‘jump’ indicates whether it is allowed to jump from this node to another node in a subject in this interleave level. An ‘early end of subject’ indicates that it is allowed to go from this node to a node in one of subjects at the same interleave level and if there are no other subjects in the same interleave, that it is possible to jump to a node in a subject in the next interleave. An ‘end of scenario’ indicates that the scenario is terminated after this statement. A combination of these features allows for variability and expressiveness in a scenario.
A domain expert can then export valid scenarios in XML format. Scripts may be saved locally and imported to modify and continue development. The output of the editor, a dialogue, is stored as an XML file that follows the schema:
https://github.com/UUDSL/scenario/blob/master/scenarioLanguage.xsd
Date: Jun 30, 2016
Language: English
Access URL: https://github.com/UURAGE/ScenarioEditor
Download: Dialogue-Scenario-Editor.zip
editor
communication
authoring tool
browser
XML
Source code:
Documentation:
Setup files:
Test:
Game development environment: Other
Target platform: Browser
Programming language: JavaScript
Version: 4.0
Version notes:
With the latest release (v4.0) of the component, an instance of this editor can be configured catering to the specific needs of a game developer. A game developer can specify virtual character(s), properties (e.g. name of a character) and parameters (e.g. score) specific to their game needs.
• Scores and emotions can be configured as parameters of scenarios, which can be modified at a statement.
• Properties of a scenario can be configured. For example, you can specify the name of a character.
Development status: Under Development
Commit URL: https://github.com/UURAGE/ScenarioEditor
Type: Apache 2.0 (Apache License 2.0)
URL: https://github.com/UURAGE/ScenarioEditor/blob/master/LICENSE.txt